The following list of variables can be selected for display when a data file is plotted. Note that this table is not representative of all the variables displayed in TRIOS; it represents only a selection of the available variables.
Rheology Variables
| Variable
|
Symbol
|
Description
|
Applicability
|
| Angular frequency |
w (rad/s) |
Frequency expressed as rad/s |
Oscillation |
| Axial Force (*) |
F |
Force in axial direction |
|
| Force |
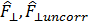
|
Oscillation force, raw and corrected for compliance and inertia |
Oscillation axial |
| Phase angle |
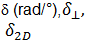
|
Phase angle. The phase difference between the stress and strain in an oscillatory test. A measure of the presence and extent of elastic behavior in a fluid. |
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Tan Delta (Loss) |
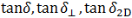
|
This is the tangent of the phase angle |
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Strain (input) |
gº
|
General term for the geometry-dependent, sinusoidal rotational displacement applied
to the sample by the actuator. Strain is the product of the strain constant and the
angular displacement. |
Step, Flow |
| Strain amplitude |
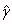
|
idem |
Oscillation |
| Orthogonal strain amplitude |
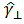
|
|
Oscillation in axial direction |
| 2D strain amplitude |
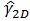
|
|
Oscillation in arbitrary direction |
| Strain (result) |
g
|
idem |
Step, Flow |
| Stress (input) |
so
|
General term for the geometry dependent torque applied by the sample to the transducer. Stress is the product of the stress constant and the torque.
|
Step, Flow |
| Stress (amplitude) |
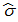
|
idem |
Oscillation |
| Orthogonal stress amplitude |
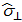
|
|
Oscillation in axial direction |
| 2D stress amplitude |
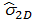
|
|
Oscillation in arbitrary direction |
| Stress (results) |
s
|
|
Step, Flow
|
| Time |
clocktime (hh:mm:ss) |
Displays the time elapsed during the experiment. |
All |
| Deltalength (mm) |
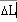
|
Method, used in conjunction with AutoTension, by which the instrument continually
corrects for changes in sample length or gap during testing over a range of temperatures.
Delta-L Tracking
functions only when AutoTension is enabled. |
All |
| Angular Displacement (result) |
q, q
|
Specifies the rotation of the actuator in reference to the origin or to the previous position. |
Step, Flow |
| Displacement [2-8] |
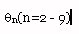
|
Absolute magnitudes of the harmonic contributions of the angular displacement signal.
|
Oscillation harmonics signal |
| Displacement amplitude |
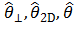
|
|
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Elongation Stress (input) |
σE0 |
|
Step |
| Elongation Stress (result) |
sE
|
|
Step |
| Elongation Force |
FE |
|
Step |
| Elongation Viscosity |
hE(t) |
|
Step |
| Elongation Strain (input) |
eo
|
|
Step |
| Elongation Strain (result) |
e
|
Cauchy strain |
Step |
| Hencky Strain (input) |
eHo
|
|
Step |
| Hencky Strain (result) |
eH
|
|
Step |
| Frequency (Hz) |
f |
Frequency expressed in Hz
|
Oscillation |
| Storage Modulus |
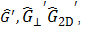
|
Elastic (storage) modulus: The contribution of elastic (solid-like) behavior to the complex modulus
See also: |
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Loss Modulus |
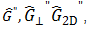
|
Viscous (loss) modulus: The contribution of viscous (liquid-like) behavior to the Complex Modulus. See also: |
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Complex Viscosity |
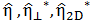
|
Complex viscosity. The complex modulus divided by the angular frequency. |
Oscillation, angular, axial, arbitrary |
| Complex Modulus |
|G*| |
Complex modulus: The overall resistance to deformation of a material, regardless of whether that deformation is recoverable (elastic) or non-recoverable (viscous).
|
Oscillation |
| gap |
|
The distance between the upper and lower geometries. |
Oscillation, Step, Flow |
| Harmonic phase angle [2-8] |
φn(n=2 - 9)
|
Phase of the harmonic torque signal referred to the sin of the fundamental torque
|
Oscillation harmonics signal |
| Shear Storage Compliance |
J' |
Storage compliance. See also: |
Oscillation |
| Shear Loss Compliance |
J" |
Loss compliance. See also: |
Oscillation |
| Complex Compliance |
|J*| |
|
Oscillation |
| Compliance |
J(t) |
|
Transient |
| Viscosity (result) |
h
h(t)
|
|
Flow
Step
|
| Dynamic Viscosity |
h' |
Real part of dynamic (complex) viscosity |
Oscillation |
| Out of phase component of h* |
h" |
Imaginary part of dynamic (complex) viscosity |
Oscillation |
| Complex Viscosity |
|η*| |
Dynamic (complex) viscosity |
Oscillation |
| Normal Force (*) |
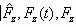
|
Tensile-compressive energy that is expended by the sample due to the shear deformation. Normal force is measured, in steady, transient and oscillation mode by the transducer. |
Oscillation, Flow |
| Normal Stress (result) |
N1 |
|
Step, Flow |
| Normal Stress Coefficient |
ψ(t)
|
|
Step
Flow
|
| Oscillation Stress Amplitude |
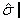
|
|
Oscillation |
| Oscillation Stress (sample) |
s (sample)
|
|
Oscillation |
| Oscillation Torque |
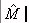
|
|
Oscillation |
| Oscillation Torque [2-8] |
Mn n = 2 - 9 |
Absolute magnitude of the harmonics of the torque signal
|
Oscillation harmonics signal |
|
Oscillation Torque [2-8] Ratio
|
In/I1 n = 2 - 9 |
Relative magnitude of the harmonics of the torque signal. They are defined by the ratio of absolute magnitude of the harmonic n and the fundamental (n=1)
|
Oscillation harmonics signal |
|
Rawphase (displacement) torque
(Xducer displacement)
|
|
Raw phase values for the signals measured during an oscillation test. The raw phases for fundamental and harmonics are all referred to the sin reference signal
|
Oscillation |
| ShearRate (result) |

|
The rate of change of shear stress. The velocity gradient perpendicular to the direction of shear flow (dv/dx). |
Step, Flow |
| Shear Rate (set) |
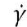 o o
|
|
Flow, Step |
| StatusBits |
|
Coded status information about the test
|
All |
| tan(d) |
Loss |
The tangent of the phase angle – the ratio of viscous modulus to elastic modulus and a useful quantifier of the presence and extent of elasticity in a fluid.
|
Oscillation |
| Temperature |
T
|
Temperature used for the experiment. |
All |
| Time |
t |
Time starting when the first motor command is issued during the experiment. |
All |
| Torque |
M |
Moment that is applied to the sample during deformation. |
Flow |
| Velocity |
W
|
|
Flow |
| Velocity (input) |
Wo
|
|
Flow |
| Xducerdisplacement |
|
Magnitude of transducer radial movement induced by sample during deformation. |
Oscillation |
| Xducercompliance phase [2-8] |
|
|
Oscillation harmonics signal |
| Step time (s) |
ts
|
Time starting at the beginning of each step in a procedure. |
All |
(*) Axial force in contrast to the Normal force is not used to calculate the material behavior. Axial force is measured differently by the instrument and is used to control test performance such as gap changes during AutoTension or gap setting during sample loading.
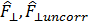
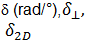
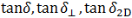
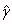
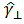
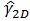
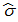
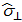
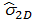
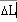
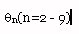
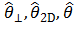
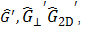
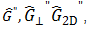
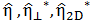
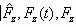
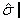
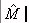

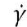 o
o
